近日,深圳大学化学与环境工程学院李倍老师在领域顶级期刊《IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems》(影响因子7.9,中科院1区,TOP期刊)上发表了题为《Real-Time Hydrogen Refuelling of the Fuel Cell Electric Vehicle Through the Coupled Transportation Network and Power System》的研究论文。李倍为独立第一作者。深圳大学为第一单位。其他作者包括Jiangchen Li, Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, China;Zhixiong Li, Opole University of Technology, Poland;Miguel Angel Sotelo, University of Alcalá, Spain。
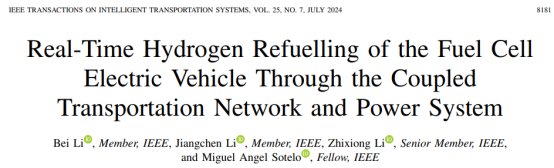
HFCEV的加氢仍然是一个亟待解决的问题。本文提出一种基于氢电微网来生产氢气,为HFCEV加氢,并提出了不同的策略来引导HFCEV在交通网络与电力系统耦合下的加氢行为。首先,根据实际交通网络构建HFCEV交通流模型。其次,建立实时仿真算法。第三,构建基于氢气的微电网为HFCEV加氢。第四,建立IEEE 30节点电网输出功率模型。最后,提出通过交通网络与电力网络的耦合实现HFCEV实时加氢。耦合结构如图1,并比较了不同的HFCEV加氢策略(固定价格、动态价格、LSTM决策价格)。结果表明,在动态价格下,交通网络的拥堵得到改善,等待时间减少了17.71%,网络的时间损失减少了13.29%。通过合理的价格引导,车辆会选择指定的站点进行氢气加注,并影响交通网络车流量的时空分布。此外,通过调整发电站输出功率和加氢站输入功率,可以改善电力系统的电压条件。
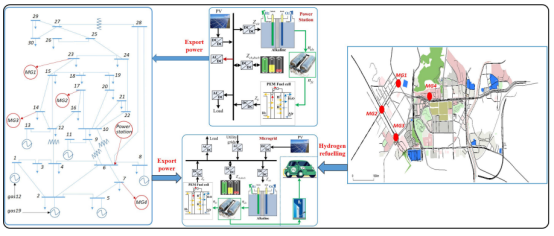
图1、电网-微网-交通网耦合结构
分析了四种不同的电网耦合交通网结构如下图2所示:
1) In Case 1, the power station is not considered, only microgrids are considered;
2) In Case 2, the power station is considered, the exporting power of the power station is adjusted based on the selling price, and the selling price is adjusted based on the utility grid voltage; in addition, in microgrid, the hydrogen price is adjusted based on the traffic congestion;
3) In Case 3, the power station is considered, the difference is that in the microgrid, the hydrogen price is adjusted based on the utility grid voltage and the traffic congestion;
4) In Case 4, an LSTM network is adopted to train the relationship between states (voltage, traffic flow) and the price. The hydrogen price is decided based on the smart LSTM network.
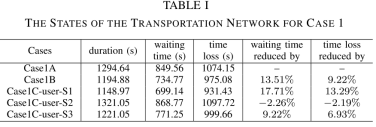
此外,在Case 1中3种不同的价格场景Case 1A, Case 1B, and Case 1C被进行比较,包括:
Case 1A:hydrogen price is not considered, and vehicles choose the nearest distance station to refuel hydrogen;
Case 1B:fixed hydrogen price is considered;
Case 1C:dynamic hydrogen price is considered, and the price is dynamically adjusted based
on the traffic congestion. Three different users choosing refuelling station strategies are compared.
图2、电网耦合交通网的不同场景
结果:在不同场景下的交通网状态如表1所示;电网的电压偏移情况如下图所示。
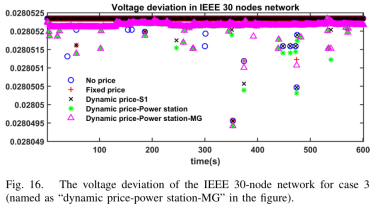
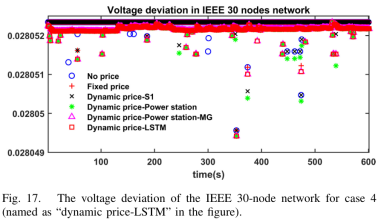
原文链接:https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10557141
李倍曾于2015-2019年在法国国家科学研究中心(CNRS)Femto-st, FCLAB实验室从事科学研究。目前担任深圳大学能源科学与工程系教师。至今以独立第一作者发表SCI/EI英文论文30余篇,独立第一作者SCI期刊论文18篇,包括IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, eTransportation, Applied energy等国际知名期刊,其中包括一篇ESI高被引论文。